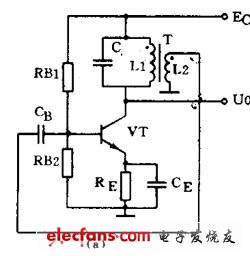
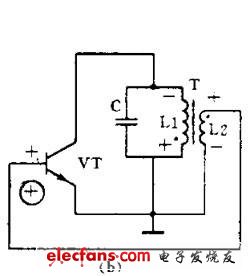
Oscillation circuit use and oscillation conditions A circuit that automatically converts DC power into an AC signal having a certain amplitude and a certain frequency without an external signal is called an oscillation circuit or an oscillator. This phenomenon is also called self-oscillation. In other words, a circuit capable of generating an AC signal is called an oscillation circuit. An oscillator must consist of three parts: an amplifier, a positive feedback circuit, and a frequency selective network. The amplifier can amplify the input signal applied to the oscillator input to maintain a constant value of the output signal. The positive feedback circuit ensures that the feedback signal supplied to the input of the oscillator is of the same phase, in order to maintain the oscillation. The frequency selective network only allows a certain frequency f 0 to pass, allowing the oscillator to produce a single frequency output. Whether the oscillator can oscillate and maintain a stable output is determined by the following two conditions; one is that the feedback voltage uf and the input voltage U i are equal, which is the amplitude balance condition. Second, uf and ui must be in the same phase. This is a phase equilibrium condition, which means that it must be guaranteed to be positive feedback. Under normal circumstances, the amplitude balance condition is often easy to do, so in judging whether an oscillation circuit can oscillate, it is mainly to see whether its phase balance condition is established. The oscillator can be divided into ultra-low frequency (below 20 Hz), low frequency (20 Hz to 200 kHz), high frequency (200 kHz to 30 MHz) and ultra high frequency (10 megahertz to 350 megahertz) according to the oscillation frequency. Kind. According to the oscillation waveform, it can be divided into two types: sine wave oscillation and non-sine wave oscillation. The sine wave oscillator can be divided into an LC oscillator, an RC oscillator, and a quartz crystal oscillator according to the components used in the frequency selective network. Quartz crystal oscillators have high frequency stability and are only used in demanding applications. In general household appliances, various LC oscillators and RC oscillators are used in large quantities. LC oscillator The frequency selective network of the LC oscillator is an LC resonant circuit. Their oscillation frequency is relatively high, and there are three common circuits. (1) Transformer feedback LC oscillating circuit Figure 1 (a) shows the transformer feedback LC oscillating circuit. Transistor VT is a common emitter amplifier. The primary of transformer T is the LC resonant circuit that acts as a frequency selective, and the secondary of transformer T provides a positive feedback signal to the amplifier input. When the power is turned on, a weak transient current appears in the LC loop, but only the current with the same frequency and loop resonance frequency f 0 can generate a higher voltage across the loop. This voltage is coupled through the primary and secondary L1 and L2 of the transformer. Returned to the base of transistor V. It can be seen from Fig. 1(b) that as long as there is no error in the connection, the feedback signal voltage is the same as the phase of the input signal voltage, that is, it is positive feedback. Therefore, the oscillation of the circuit is rapidly strengthened and finally stabilized. The characteristic of the transformer feedback LC oscillating circuit is that the frequency range is wide and it is easy to start, but the frequency stability is not high. Its oscillation frequency is: f 0 =1 / 2Ï€ LC . It is commonly used to generate sinusoidal signals from tens of kilohertz to tens of megahertz. Air Humidifier,Ultrasonic Air Humidifier,Air Humidifier For Home,Mini Usb Air Humidifier Guangdong Aiyimi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.nbminifan.com